
The main disadvantages of a semi-closed greenhouse are:
o Considerably higher initial investment costs for setup.
o Regular maintenance requirements for the sophisticated equipment.
o The potential loss of these benefits if the greenhouse is not installed in a suitable climate.
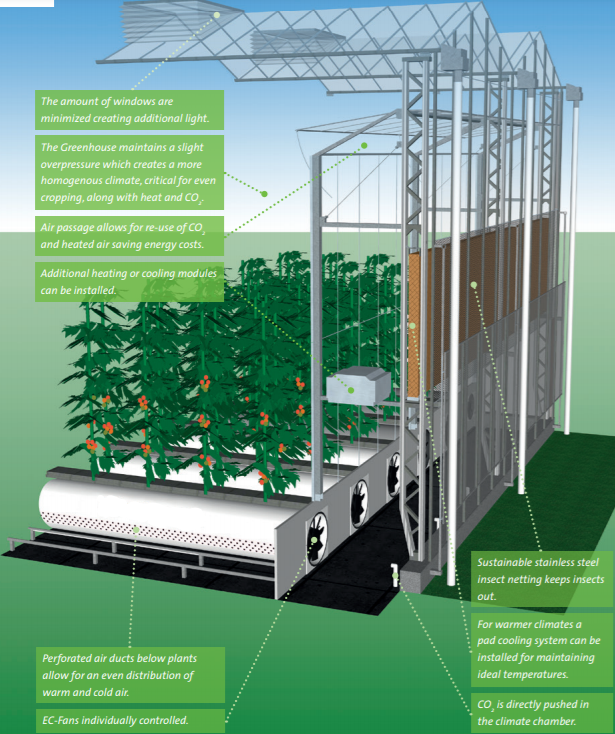
Semi-closed greenhouse unique aspect is the corridor located along the outer gable end walls of the greenhouse, which utilizes external air for cooling and dehumidification. This corridor acts as a mixing chamber, blending the cool, dry air from outside with the warm, moist air from within the greenhouse. Consequently, the air that is circulated back into the greenhouse becomes cooler and drier.
Here's a comparison between Semi-Closed Greenhouses and Traditional Venlo Greenhouses across various parameters
While Venlo-type greenhouses are a specific design known for their structural efficiency and high light transmittance, semi-closed greenhouses focus more on advanced climate control and energy efficiency, offering a more controlled environment for plant growth. The choice between the two often depends on the specific requirements of the crops, local climate conditions, and energy considerations.Выбор между этими двумя типами часто зависит от конкретных требований к культурам, местных климатических условий и энергетических соображений.